
The planets would be moving in straight lines, but the sun’s gravity pulls them toward it. Any moving object in space will travel in a straight line at the same speed forever, planets included. Newton’s First Law of Motion states that a body in motion keeps the same motion unless acted upon by an outside force. What is the Newton’s law of motion in relation to planetary Motion? Newton’s First Law of Motion – if an object is at rest, it takes un- balanced forces to make it move. Newton’s First Law of Motion explains how the satellite remains in orbit. This keeps the satellite circling in its orbit. How do orbits relate to Newton’s first law of motion?Ī satellite has its forward thrust, which is offset by the pull of gravity towards the earth. Newton’s law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Attraction is directly proportional to the product of their masses. The Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton’s law of gravity): 1. Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity explains how gravity works by describing gravity as the effect of curvature of four dimensional spacetime. A theory is an explanation of a natural phenomenon. This is a law because it describes the force but makes not attempt to explain how the force works. What is the difference between the law of gravity and the theory of gravity? Orbits of planets (and everything else) are a balance between the moving object’s tendency to move in a straight line at constant speed (Newton’s 1st law) and the gravitational pull of the other object (see below). How does gravity and Newton’s 1st law relate to our universe? According to Newton’s 3rd law, the stone also exerts an equal force on the Earth, but towards itself. When a stone falls from a certain height above the Earth’s surface, it accelerates towards the center of Earth under the influence of Earth’s gravity. In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction. In the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. In the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. What are the 3 laws of motion and gravity?

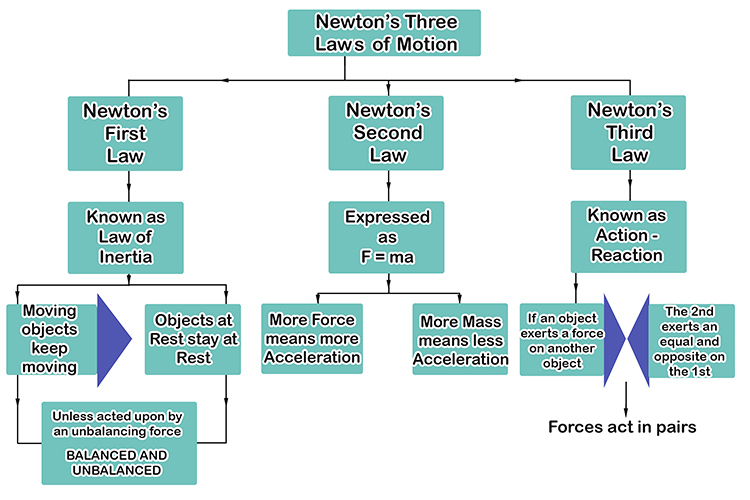
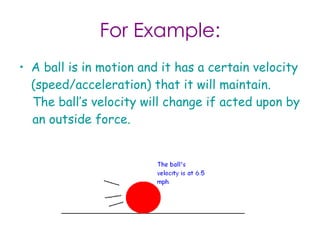
This is due to the frictional force between the road and the tire.Īccording the the conservation of energy theory, energy cannot be created or destroyed. If you are unsure about all of the forces that act, search google to help you figure out which forces act and then label them with arrows in your diagram.īicycle with thick tires, like mountain bikes, tend to go slower than bicycles with thin tires, like road bikes, when you apply the same amount of force, even if the bicycles are the same weight. Vector diagrams are pictures which include vector arrows to represent all of the forces which act on a single object.ĭraw a vector diagram of a bicycle being pedaled and label all of the forces which act on it. Vectors are represented by arrows and can be added if they face in the same direction or subtracted if they are in the opposite directions. Since forces have both Magnitude (Size) and direction, they are said to be vector quantities. It is helpful when describing forces acting on an object to label their direction. The ideas have been tested and verified so many times over the years that scientists now call them Newton's Three Laws of Motion. In his work, he came up with the three basic ideas that we still use to describe the physics of motion ( up to a point). He worked on developing both calculus and physics at the same time. A little bit stuffy, bad hair, but quite an intelligent guy. There was this fellow in England named Sir Isaac Newton.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
